|
|
U
Ulama (plural), Alim (single) Islamic scholars.
Umbanda is related to and has many similitudes with other Afro-Brazilian religions like Candomblé, Batuque, Macumba, Quimbanda, Xambá, Egungun, Ifá, Irmandade, Confraria, Xangô do Nordeste and Tambor de Mina, but also has it own identity. Although some of its beliefs and most of its practices existed in the late 19th century in almost all Brazil, it is assumed that Umbanda originated in Rio de Janeiro and surrounding areas in the early 20th century, mainly due to the work of a psychic (medium), Zélio Fernandino de Moraes, who practiced Umbanda among the poor Afro-Brazilian population. Since then, Umbanda has spread across mainly southern Brazil and even to foreign countries like Uruguay and Argentina. Umbanda has many branches, each one with a different set of believes and practices. Some of the Umbanda's basic beliefs are the existence of a One Supreme Creator God (the Orixá Olorum); deities called Orixás related to Catholic Saints that act as God's energy and plain power expansions; spirits of deceased people that counsel and guide believers through troubles in our material world; psychics called mediums who have a natural ability that can be perfected to bring messages from the spiritual world of Orixás and guiding spirits, reincarnation and spiritual evolution through many material lives (Karmic Law) and the practice of Charity. The information here presented is just a general view of all Umbanda branches, so some beliefs and practices here described could be different from those observed in a specific place.
Unconditional election is the Calvinist teaching that before God created the world, he chose to save some people according to his own purposes and apart from any conditions related to those persons. Unconditional election is drawn from the doctrines of salvation developed by Augustine of Hippo, was first codified in the Belgic Confession (1561), re-affirmed in the Canons of Dort (1619), which arose from the Quinquarticular Controversy, and is represented in the various Reformed confessions such as the Westminster Standards (1646).
Undead is a collective name for fictional, mythological, or legendary beings that are deceased yet behave as if alive. Undead may be incorporeal, such as ghosts, or corporeal, such as vampires and zombies. Undead are featured in the legends of most cultures and in many works of fantasy and horror fiction. Most commonly, it is now taken to refer to supernatural beings which had at one time been alive and continue to display some aspects of life after death, but the usage is highly variable.
1. An adherent
of Unitarian Universalism. This term is sometimes used to refer to the belief that the Christian God is a unity, not a Trinity. This was a near-universal belief in the very early Christian movement, but was narrowly voted down at an early church council in the fourth century CE. By popular vote, and a bit of political arm twisting, God was perceived as multiple persons in one entity. A more common modern usage is to refer to the members and congregations associated with the Unitarian Universalist Association (UUA) in the U.S. or the Canadian Unitarian Council in Canada. They promote a creedless religion in which members are expected to develop their personal spirituality, moral standards and religious beliefs. The purpose of the minister in Unitarian congregations is not to teach what the membership should believe. It is to help the congregation develop spiritually and religiously. Many articles and books by non UUA members mistakenly propagate the belief that the UUA teaches the unity of God. In fact, most UUA followers are Humanists and do not believe in a personal deity.
See also Calvinism, Universalism.
See also Cosmological argument and The Five Ways
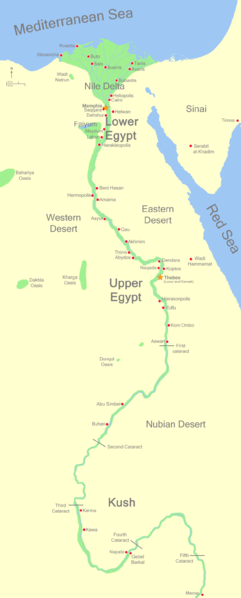
Upper Egypt See Upper Egypt
Ur of the Chaldees See Ur Kas'dim below
Ur Kas'dim is mentioned four times in the Tanakh or Old Testament, with the distinction "Kas'dim" traditionally rendered in English as "of the Chaldees", referring to the Chaldeans. In Genesis, the name is found in 11:28, 11:31 and 15:7. In Nehemiah 9:7, a single passage mentioning Ur Kas'dim is a paraphrase of Genesis. Although not explicitly stated in the Tanakh it is generally understood to be the place where Abraham was born. (Genesis 11:27-31 names it as the birthplace of Abraham's brother Haran, and the point of departure of Abraham's family.) The Book of Jubilees states that Ur Kas'dim was founded in 1687 Anno Mundi (year of the world) by 'Ur son of Kes'ed, presumably the offspring of Arphaxad, adding that in this same year, wars began on Earth. Although Arphaxad himself is recorded to have been born 2 years after Noah's Flood of 1656 AM and so aged just 29 in 1687. "And 'Ur, the son of Kes'ed, built the city of 'Ara of the Chaldees, and called its name after his own name and the name of his father. (ie, Ur Kas'dim = Ur of the Kes'eds)" (Jubilees 11:3) It also represents Abraham's immediate ancestors as dwelling in Ur Kas'dim beginning with his great-grandfather, Serug. Jewish sources say very little about the location of Ur Kas'dim. In Genesis 12:1, after Abraham and his father Terah have left Ur Kas'dim for the city of Haran (spelled differently in the Hebrew text than the name of Abraham's brother) in Aram-Naharaim, God instructs him to leave his land, his moladet, and his father's house. The traditional Jewish understanding of the word moladet is "birthplace". n Genesis 24:4-10, similarly, Abraham instructs his servant to bring a wife for Isaac from his land and moladet, and the servant departs for Aram Naharaim. The general Jewish understanding is thus that the birthplace lay in Aram Naharaim. This view was noted in particular by Nachmanides (Ramban). This understanding of the term moladet as "birthplace" is not universally agreed; most translations, from the Septuagint to modern English versions, typically render it as "kindred" or "family". However, a further reference in Genesis 24 to the area of Aram Naharaim as being the eretz moladet, i.e. "land of nativity" of Abraham from which a wife is to be found for Isaac, appears to corroborate the traditional Jewish understanding. The Talmud (Yoma 10a) identifies the Biblical city of Erech with a place called "Urichus". T. G. Pinches in The Old Testament in the Light of the Historical Records and Legends of Assyria and Babylonia and A. T. Clay, writing in the International Standard Bible Encyclopedia article Ur of the Chaldees, understood this as an identification of Uruk (modern Warka) or Biblical Erech with Ur Kas'dim. However no tradition exists equating Ur Kas'dim with Urichus and the latter is understood by modern scholars as a reference to Uruk which is indeed identified with Erech. The traditional site of Abraham's birth according to Islamic tradition is a cave in the vicinity of the ancient Seleucid city of Edessa. Edessa is now named S,anl?urfa, and the cave lies near the centre of this modern city and is the site of a mosque called the Mosque of Abraham. The Turkish name Urfa for the city is derived from earlier Syriac, Orha-y and Greek, Orrha. The tradition connecting Ur Kas'dim with the site is not exclusively Islamic, the 18th century anthropologist Richard Pococke noted in his Description of the East, that it was the universal opinion of the Jews that Urfa was Ur Kas'dim. Scholars are skeptical of the identification of Ur Kas'dim with Urfa. Although the origin of the Greek and Syriac names of the city are uncertain, they appear to be based on a native form, Osroe, the name of a legendary founder, the Armenian form of the Persian name Khosrau (Chosroes). Similarity with "Ur" would thus be accidental.
This is the ancient land where Job lived, sometime after The Flood. It is mentioned in the Bible in these three verses: 1:1; Jer. 25:20; Lam. 4:21. It may have been named after Uz, the son of Aram, who settled this region. Genesis 36:20-21 seems to indicate that this area was conquered by Horites and eventually Edomites, and became known as Edom (Lamentations 4:21).
DISCLAIMER: PLEASE READ I make no claim to be an expert pertaining to the knowledge and information of God and religion and all that which relates to God and religion. I make no claims, promises or guarantees about the completeness or adequacy of the information contained in or linked to this website and its associated sites. Nothing on this site constitutes legal or medical advice. This website is an unofficial source of news and information continually updated from thousands of sources around the net. This website is the composition of many hours of research. Information contained within this site has come from numerous sources such as websites, newspapers, books, and magazines. By printing, downloading, or using any info from this site, you agree to our full terms. Review the full terms by clicking here. Below is a summary of some of the terms. If you do not agree to the full terms, do not use the information. All information on this web site is provided as a free service. Under no conditions does it constitute professional advice. No representations are made as to the completeness, accuracy, comprehensiveness or otherwise of the information provided. This site is considered publishers of this material, not authors. Information may have errors or be outdated. Some information is from historical sources or represents opinions of the author. It is for research purposes only. The information is "AS IS", "WITH ALL FAULTS". User assumes all risk of use, damage, or injury. You agree that we have no liability for any damages. We are not liable for any consequential, incidental, indirect, or special damages. You indemnify us for claims caused by you.
This site is maintained for research
purposes only.
.
|
||||||